Camunda 7 DMN – Complete Guide with Examples
DMN (Decision Model and Notation) is a powerful standard used in Camunda 7 to automate decisions using Decision Tables, Context, Literal Expressions, and FEEL.
It separates business logic from workflow logic, making your BPMN processes cleaner, maintainable, and business friendly.
In this guide, you will learn how to create, deploy, and execute DMN tables in Camunda 7 using Java, REST, and Modeler.
⭐ What is DMN?
DMN = Decision Model and Notation
Created to:
✔ Automate business rules
✔ Externalize decision logic
✔ Allow business users to define rules
✔ Integrate with BPMN processes
✔ Support FEEL expressions (Friendly Enough Expression Language)
In Camunda, DMN is executed by the Decision Engine, which is part of the Camunda BPM platform.
1️⃣ Creating a DMN Decision Table in Camunda Modeler
A DMN table contains:
-
Inputs (values coming from the process or API)
-
Rules
-
Outputs (result of evaluation)
-
Hit Policy
-
FEEL expressions
Example Scenario
Loan Approval decision based on:
-
Credit score
-
Monthly income
-
Loan amount
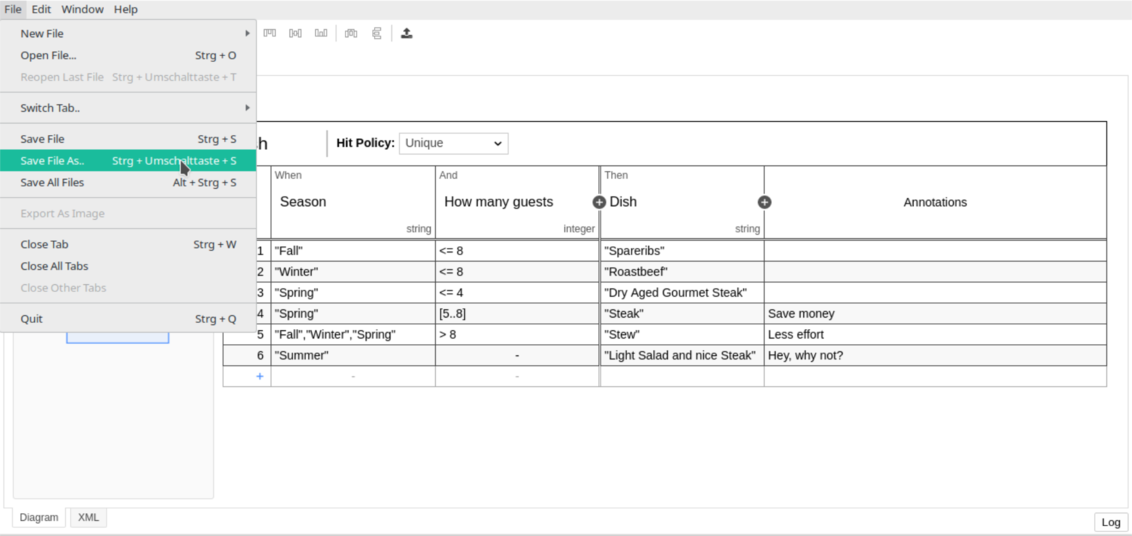
Sample DMN Table
| Credit Score | Income | Loan Amount | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| > 700 | > 50000 | < 10,00,000 | APPROVE |
| 600–700 | > 40000 | < 5,00,000 | REVIEW |
| < 600 | any | any | REJECT |
2️⃣ Understanding Hit Policies
| Hit Policy | Meaning |
|---|---|
| U – Unique | Only one rule must match |
| F – First | First matching rule wins |
| A – Any | Any matching rule may be returned |
| C – Collect | Returns list (sum, min, max, count) |
| P – Priority | Highest priority rule wins |
| R – Rule Order | Rules returned in order |
| O – Output Order | Sorted by output priority |
Most common: Unique (U) and First (F).
3️⃣ FEEL Expressions
FEEL is used inside DMN for conditions.
Examples:
| Expression | Meaning |
|---|---|
> 500 | Value greater than 500 |
[10..20] | Between 10 and 20 |
<= 1000 | Less than or equal to 1000 |
"Gold" | Matches string Gold |
not("India") | Not India |
null | Empty value |
4️⃣ Deploying a DMN Table
Place DMN file under:
Camunda auto-deploys DMN files from resources folder.
5️⃣ Calling DMN from BPMN
Add a Business Rule Task → set implementation:
✔ Decision Ref = loan_decision
✔ Result Variable = loanResult
✔ Map decision inputs via input mappings
✔ Use FEEL or script expressions
Example variable mapping:
| Input | DMN Input |
|---|---|
${creditScore} | creditScore |
${income} | income |
${amount} | loanAmount |
6️⃣ Execute DMN from Java
7️⃣ Execute DMN via REST API
8️⃣ DMN with Spring Boot
Add dependency:
Place DMN under:
Call using DecisionService as shown above.
9️⃣ Real-World Example: Credit Risk Classification
Inputs:
-
Past defaults
-
Age
-
Salary
-
Country
-
Account balance
DMN outputs:
-
HIGH_RISK
-
MEDIUM_RISK
-
LOW_RISK
This plugs directly into your BPMN workflow for automated decision routing.
🔟 Best Practices for DMN in Camunda 7
✔ Use FEEL for business-friendly logic
✔ Avoid script expressions when FEEL is enough
✔ Use Unique hit policy when rules must not overlap
✔ Use Priority hit policy for risk-based scoring
✔ Keep DMN tables small & simple
✔ Use meaningful column names
✔ Always set Result Variable when used in BPMN
✔ Store DMN models in a separate folder
✔ Add unit tests for rule validation
📌 Common Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Using Java delegates instead of DMN
❌ Missing decisionRef in Business Rule Task
❌ Wrong variable name mapping
❌ Overlapping rules without correct hit policy
❌ Using scripts instead of FEEL
❌ Hardcoding DMN values in BPMN
Rest APIs
🎉 Conclusion
DMN in Camunda 7 gives you:
✔ Clean separation between workflow and decision logic
✔ High-performance automated rules engine
✔ Business-friendly FEEL rule definitions
✔ Easy integration with Java, REST, Spring Boot
✔ Clear and maintainable decision logic
DMN makes your processes faster, smarter, and easier to maintain — a must-learn feature for every Camunda developer.
💼 Professional Support Available
If you are facing issues in real projects related to enterprise backend development or workflow automation, I provide paid consulting, production debugging, project support, and focused trainings.
Technologies covered include Java, Spring Boot, PL/SQL, Azure, and workflow automation (jBPM, Camunda BPM, RHPAM).
🌐 Website: IT Trainings | Digital metal podium


Comments
Post a Comment